What Is Produced During Glycolysis
"Glycolysis is the metabolic process that converts glucose into pyruvic acid."
What is Glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is cleaved downward to produce energy. It produces 2 molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH and water. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell and does not crave oxygen. Information technology occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms.
Glycolysis is the principal stride of cellular respiration, which occurs in all organisms. Glycolysis is followed by the Krebs cycle during aerobic respiration. In the absence of oxygen, the cells make minor amounts of ATP as glycolysis is followed by fermentation.
This metabolic pathway was discovered past 3 German biochemists- Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas in the early 19th century and is known as the EMP pathway (Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas).
Also Read:TCA wheel
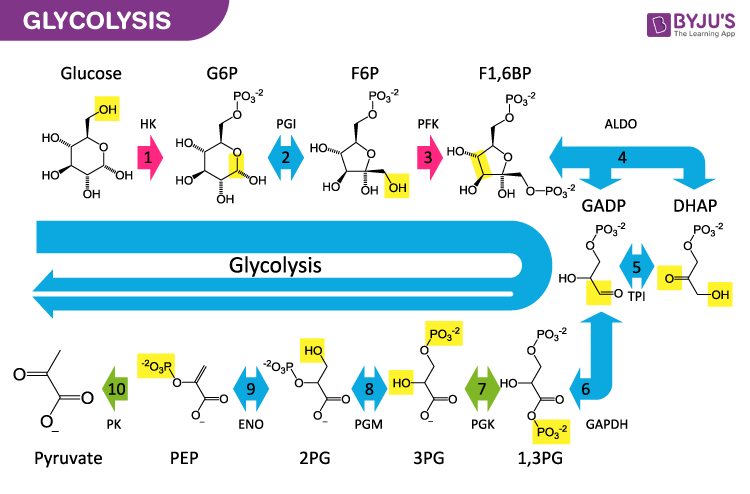
Glycolysis Pathway
The glycolysis pathway occurs in the following stages:
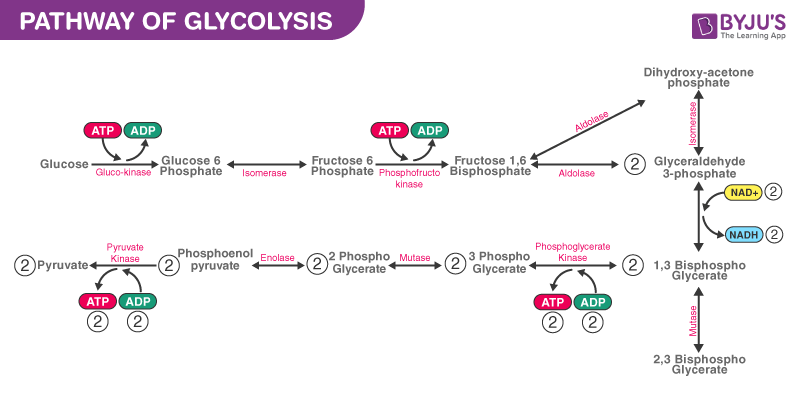
Phase one
- A phosphate grouping is added to glucose in the jail cell cytoplasm, by the action of enzyme hexokinase.
- In this, a phosphate group is transferred from ATP to glucose forming glucose,half-dozen-phosphate.
Phase 2
Glucose-6-phosphate is isomerised into fructose,six-phosphate past the enzyme phosphoglucomutase.
Phase three
The other ATP molecule transfers a phosphate grouping to fructose six-phosphate and converts it into fructose 1,six-bisphosphate by the action of the enzyme phosphofructokinase.
Stage 4
The enzyme aldolase converts fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate, which are isomers of each other.
Step 5
Triose-phosphate isomerase converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate which is the substrate in the successive step of glycolysis.
Step six
This step undergoes two reactions:
- The enzyme glyceraldehyde iii-phosphate dehydrogenase transfers one hydrogen molecule from glyceraldehyde phosphate to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide to grade NADH + H+.
- Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase adds a phosphate to the oxidised glyceraldehyde phosphate to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
Step 7
Phosphate is transferred from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP to form ATP with the help of phosphoglycerokinase. Thus two molecules of phosphoglycerate and ATP are obtained at the end of this reaction.
Stride 8
The phosphate of both the phosphoglycerate molecules is relocated from the third to the second carbon to yield two molecules of 2-phosphoglycerate past the enzyme phosphoglyceromutase.
Step ix
The enzyme enolase removes a h2o molecule from 2-phosphoglycerate to form phosphoenolpyruvate.
Step 10
A phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate is transferred to ADP to form pyruvate and ATP past the action of pyruvate kinase. Two molecules of pyruvate and ATP are obtained as the terminate products.
Fundamental Points of Glycolysis
- It is the process in which a glucose molecule is cleaved down into two molecules of pyruvate.
- The process takes identify in the cytoplasm of plant and animal cells.
- 6 enzymes are involved in the process.
- The stop products of the reaction include 2 pyruvate, ii ATP and 2 NADH molecules.
Likewise Read:Departure between Glycolysis and Kreb's wheel
To know more well-nigh glycolysis, its definition and the glycolysis pathway, keep visiting BYJU'S website.
What Is Produced During Glycolysis,
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/glycolysis/
Posted by: cannonbenty1991.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Produced During Glycolysis"
Post a Comment